Riešenia na ošetrenie vykurovaním

Industrial Gases from a Global Leader
- Global leading manufacturer of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon
- World leading producer and supplier of hydrogen and helium
- Reliable supply of industrial gases
- Excellent record of meeting on-time needs
- Industry leader in safety
- Technical support when you need it
- World-class customer service
Ask the Expert

Guido Plicht
Manažér komerčných technológií - Európa
Bright annealing of steels requires conditions that are reducing to steel oxides. Traditionally, the Ellingham diagram has been used to predict the conditions that correspond to oxidation of pure metals or reduction of their oxides. This method can be used to predict the conditions that should be reducing to iron oxides and the oxides of the alloying elements added to steels, such as chromium when stainless steels are considered. This traditional approach is not precise because it only uses thermodynamic data for pure metals and their oxides—it ignores the fact that iron and alloying elements form a solid solution. In addition, you can only determine the approximate equilibrium partial pressure ratio of hydrogen and water vapor for oxidation of a specific metal at a particular temperature.
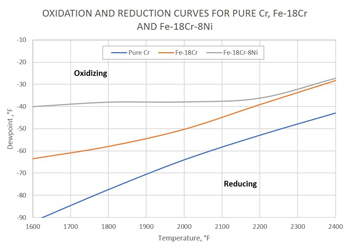
Alternatively, you can use more accurate and convenient diagrams for steels and other alloys, which are created with the help of modern databases and computer programs, such as FactSage™ (thermochemical software and database package developed jointly between Thermfact/CRCT and GTT-Technologies) or Thermo-Calc software. Using the oxidation-reduction curves, presented as dew point of pure hydrogen or nitrogen-hydrogen atmospheres versus temperature, you can quickly select the atmosphere for annealing steels without formation of oxides. The diagram in Figure 1 was calculated using FactSage. This diagram shows that oxidation-reduction curves for Fe-18%Cr and Fe-18%Cr-8%Ni systems representing stainless steels are higher than the corresponding Cr/Cr₂O₃ curves. For alloys (e.g. steels), you can achieve more precise calculations using thermodynamic data from both the pure substances (i.e. pure metals and oxides) and solutions databases. Such diagrams can be produced specifically for the steels of interest and variety of atmosphere compositions.
These methods can help you troubleshoot and optimize your annealing operation by balancing hydrogen usage versus product quality.
Oxidation-reduction curves for pure chromium, Fe-18%Cr and Fe-18%Cr-8%Ni for the total pressure of 1 atm with a hydrogen partial pressure of 0.05 atm, corresponding N₂-5% H₂. (This diagram has been produced using thermodynamic data for solutions in addition to the data for pure elements and their oxides.)
Figure 1:
PRÍPADOVÁ ŠTÚDIA
Opýtajte sa odborníka
Tvorba oxidového filmu je funkciou pomeru parciálneho tlaku vodík/voda, teploty a času, ktoré sa môžu výrazne meniť na výstupe z pece. Zvýšený rosný bod v dôsledku vstupu vzduchu pri reakcii s vodíkom v kombinácii so zníženou teplotou povedie k oxidácii, ak je čas vo výstupnej oblasti dostatočne dlhý. Navyše, vnútorný povrch hadičky sa môže ochladzovať pomalšie ako OD, čo spôsobuje nekonzistentnú oxidáciu. Protiopatrenia zahŕňajú zvýšenie rýchlosti pohybu hadičky, zvýšenie prietoku vodíka cez všetky povrchy hadičiek a aplikáciu dusíkovej clony na výstupe, aby sa riedil vstup vzduchu a pomáhalo sa chladenie. S každým protiopatrením sú spojené technologické, bezpečnostné a nákladové úvahy.

Each Atmosphere Solution is Customized for Your Needs
We can help you choose the right atmosphere composition.
- Select and provide blending and flow control equipment
- Perform on-site atmosphere analyses for consistent dimensional control, carbon control, and physical and metallurgical properties
- Optimize your furnace process to lower operating costs
- Perform state-of-the-art metallographic and chemical analyses (SEM, ESCA, SAM, ISS, SIMS)
- Provide safety training
- Test atmospheres using your parts in our lab furnaces
- Demonstrate our system at your facility
Plyny
Argon
Compressed argon gas and liquid argon in a variety of purities and in various modes of supply around the world thanks to our network of storage and transfill facilities.
Hélium
Inertný plyn pre kryogénne aplikácie, prenos tepla, tienenie, detekciu netesností, analytické a zdvíhacie aplikácie
Vodík
Cenené pre svoje reaktívne a ochranné vlastnosti a používané v mnohých priemyselných odvetviach, ako je elektronika, potraviny, sklárstvo, chemikálie, rafinácia a ďalšie, môžu ťažiť zo svojich jedinečných vlastností na zlepšenie kvality, optimalizáciu výkonu a zníženie nákladov.
Dusík
Užitočný ako plyn, pre svoje inertné vlastnosti a ako kvapalina na chladenie a mrazenie. Prakticky každé odvetvie môže ťažiť z jeho jedinečných vlastností na zlepšenie výnosov, optimalizáciu výkonu a zvýšenie bezpečnosti prevádzky.
Spojte sa s našimi technickými odborníkmi.
Kontaktujte nás a využite desiatky rokov skúseností s žíhaním.
